Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.
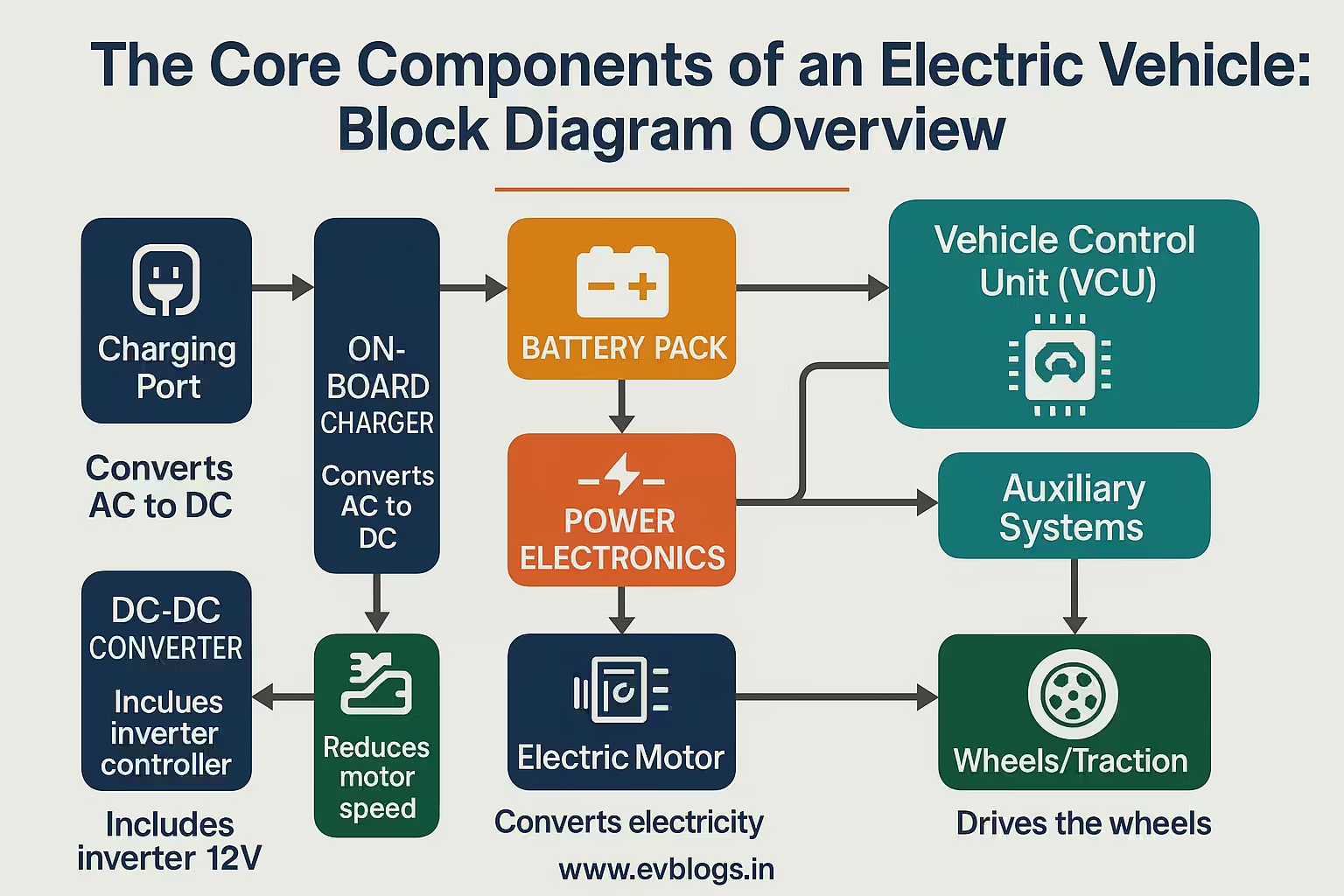
What is Block Diagram of Electric Vehicle?
Introduction: The Electric car Revolution
The days are long gone when electric vehicles were a far-fetched idea: today, EVs are already here and steer our world toward cleaner, quieter, and greener future. Electric cars are assuming the declined role of the gas-powered cars in the cities, highways, and even within the emerging economy. But, as they seem to most people the wizardry behind the hood of an electric vehicle is a mystery. So what is it that propels an EV and how do its core components work together?
Block diagram of an electric vehicle is very simple yet important key to understanding this technology. Even as a curious car owner or an aspiring engineer, or on the verge of purchasing an EV, decoding the EV block diagram will remove certain levels of mystery you might have about how these innovative cars work. In this guide we would elaborate on each and every component in the diagram, offer the professional commentary to it and offer helpful tips to both the drivers and the enthusiasts.
Just What is Electric Vehicle Block Diagram?
What is it and why?
A block diagram A block diagram is an abstract graphic that indicates the most critical constituents in a system and the relationship between them. As examples, in the case of an electric vehicle, block diagram is a graphical illustration of the drivetrain, the control systems, the energy storage, the power electronics and auxiliary systems. It provides:
- Analytical plan of learning and problem solving
- An initial point of departure in the design of the various EV systems or in making comparisons
- Perceptions of how individual units affected the performance as well as the efficiency of a vehicle
One of the significant aspects that should be perceived to make adequate decisions about owning/ maintaining/ or engineering of EV is the diagram of the blocks.
The Block Diagram A Basic Utility of the Major Networks in an Electric Vehicle
Blocks may vary, but generally an electric vehicle may be illustrated as having:
- Power (Battery pack ).
- Inverter, Converter (Power Electronics)
- Electric Motor
- Transmission ( Simple or Single-Speed Gearbox)
- Vehicle Control Unit (VCU )
- Auxiliary Systems (HVAC, 12V systems etc.)
- Charging System (On-board charger,external supply input)
- Regenerative Braking
The functional flow has a generic layout as follows:
[Charging Port]> [On-Board Charger]> [Battery Pack]> [DC-DC Converter]> [12V Auxiliary Systems] ↓ [Inverter/Controller] ↓ [Electric Motor] ↓ [Transmission] ↓ [Wheels/Traction] Now, each of the parts will be analyzed.
The Block Diagram of Electric Vehicle is Deconstructed
1. Battery Pack (Centre of Power)
Meaning of It.
An EV is designed around the battery pack as a location of energy supply. What are the most popular batteries - they are Lithium-ion, treasured with their energy density, long life, and safety.
Key Facts
- Nominal voltage: The current modern EVs are in the range of 200-800V nominal.
- Capacity.: The range is between 20 kWh (small EVs) to up to 200 kWh (large trucks).
- Thermal control: Most of the packs have a special mechanism to regulate temperature.
Real-World Impact
- Straightly linked with battery volume and potency.
- Lifespan: Packs that are well cared after can last between 8-15 years.
- Cost Cost is generally the most expensive single element in an EV and that is the battery packs.
Practical Tip:
Upgrade your vehicle software and charge according to the battery recommendations provided by the manufacturer so as to guarantee maximum battery life.
2. Charging System
What Is It
Controls the incoming power by charging.
Components
- Charging port: The charging ports may have AC or DC power intake.
- Onboard charger (OBC): It converts AC power out of the wall receptacle to a DC power to charge the battery.
- Charging controller: Maintains the current charging rate, safety and health of the battery.
Insights
- The speed of chargings is determined by the OBC capacity, and an outside source (Level 1, 2, or DC Fast).
- Some EVs have the capability to support bidirectional charging (vehicle-to-grid).
Use-Case:
The latest EVs boast fast-charging on the intercity rhythms to replenish 80 percent of the battery in 30-40 minutes.
3. Power Electronics (inverter and Dc-DC converter)
Inverter
- Takes high voltage DC of the battery to three phase AC, which most electric motors require.
- The use of variable frequency drive controls motor speeds and torques.
DC-DC Converter
- Reduces the high-voltage pack energy to 12V, or 48V to power secondary (auxiliary loads; lights, infotainment, HVAC).
Benefits
- Enables precision motor control accelerate, re-gen brake.
- Offers the defense against the low voltage operations of exposing them to high voltages.
4. Electric Motor
So What It Is
The drivetrain engine heart, as opposed to internal combustion engine.
Common Types
- Induction Motor (e.g. Tesla Model S)
- Permanent magnet synchronous (PMSM, e.g. Nissan Leaf)
- Switched Reluctance motor (Constructor_ug:Switched Reluctance Motor (emerging designs))
Function
Converts the electrical energy to the rotational energy to drive the vehicle.
Benefits
- Torque able to sprint to near instantaneous.
- High efficiency (85-95%) as compared to normal ICE (25-30%).
5. Transmission, and Differential
Overview
A majority of EVs are equipped with a single-speed gearbox (reduction gear), because electric motors have a wide range of torque.
Multi-speed transmission is also applied in Performance EVs.
Function
- Inputs the power in the motor to the drive wheels.
- The differential facilitates the capability of the wheels to move at different rates in case of cornering.
Practical Advice:
Fewer moving parts in the EV transmissions imply an easier maintenance and assurance of reliability.
6. So I have found a nice large Volvo Control Unit (VCU) And Other Controllers
What It Is
The VCU acts as the brain to provide communication between battery, power electronics, motor and auxiliary systems.
Functions
- Regulates the battery safety, the motor, regenerative braking.
- The techniques of working with driver controls (accelerator, brakes) and sophisticated characteristics (cruise control, traction/stability systems).
Benefits
Sophisticated performance, fuel economy and adaptation of current driver-assist technologies.
7. Auxiliary Systems
Components
- The 12/48V sub-systems include Luminaires, Infotainment, essuie-bords, functions of security.
- Heating, ventilating, and air conditioning, (typically with heat pumps), to conserve energy.
- Thermal management: Ensures thermal range of batteries, electronics is within the acceptable range.
Insights
Working auxiliary systems produce a strict impact on the driving range under the extreme conditions.
8. Regenerative Braking
Function
Using kinetic braking transfers about 80 percent of the braking energy to electricity.
The energy regained is accumulated into the battery which generally retrieves 10-30 percent of the braking energy expended.
Comparison Table Conventional Brakes vs regenerative brakes
| Brakes concept | Conventional Brakes | Regenerative Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| It has Recovery Energy | Energy Transduces energy to electricity | |
| Maintenance | Very high (pads/discs wear out) | Less wear, increased life |
| Modulation/Consistent and less efficient | Modulatable (blended) |
Comparison of Electric Vehicles differences in Block diagrams.
Layout of the powertrain can differ by specific vehicle design:
- Front-wheel-drives: the motor and transmission are in the front.
- Rear-wheel drive EVs: Typical of performance based EVs.
- All-wheel-drive / Dual-motor: Single motors on each axle that is controlled by control electronics to provide optimum traction.
- Special design can be involved.
Other additions:
- Fuel cells: FCEVs.
- Supercapacitors: To address peak, or regenerative spikes.
Professional Perspectives
- Al Tabsler, Manager of Employee Development, ABN AMRO Bank, says the block diagram is important because it is student-centered and prepares those students to coach other students.
- JulzR on the Drivers and Buyers case
Based on the block diagram, one can understand how an EV can deliver performance, range, safety, and economy when it comes to maintenance.
Straightforward guidance and down to business Applications
Present EV Consumers
- Become familiar with the block diagram in order to make sense of dashboard indicators or service messages.
- Exploit fully regenerative braking to extend the range and the life of the brake pads.
- However, pre-condition your battery before you fast charge in harsh weather conditions, to protect battery life.
Prospective Buyers
- Make sure that the characteristics of the cars are appropriate to meet your demands: battery scale, power charging rate, motor type, and thermal control.
- You should also ask your dealer about efficiency of their auxiliary system as it can play a role in affecting real world range.
Do-IT (® kamis 279)
- Read conversion kits block diagrams, in event you desire to retrofit or build your own EV.
- Safety measures should be under consideration at all times and EVs carry high volt systems and are hazardous.
Electric Vehicle Block Diagram, Dual Internal Combustion Block Diagrams
| Component Block Diagram EV | Component Block Diagram ICE |
|---|---|
| Power Generator | Power Supply The Tank |
| Energy conversion | Electric-motor and inverter |
| The Number of Movable components | Small (motor, reduction gear) |
| Required Periodic Maintenance | Low |
| Emissions/No tail pipe emissions | CO 2, NO x and particulates |
| Regenerative Braking | Yes |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What part of an electric car is the most expensive?
The battery pack can occupy the highest portion of the total cost and it may share up to 40 percent of the vehicle costs.
What is regenerative braking EV block diagram?
When decelerating the electric motor operates in generator mode and the resulting energy is used to recharge the batteries in converter and control electronics.
How do you make an EV charge?
Charging control has a charging port, on-board charger (AC charging) and a charging controller to manage battery health and electrical safety.
Is it possible to #x191Reportoptions description compensation suggestion star binding principal to upgrade these blocks myself?
Non-high-voltage systems (such as infotainment or 12V accessories) can be updated by the user, whereas power electronics, batteries and motors must only be serviced/upgraded by authorized professionals since such activities pose a potential hazard.
Are the block diagrams the same in all the EVs?
System functions involved are broadly the same, but the details may depend on vehicle architecture (such as dual-motor AWD drive system as found in Tesla versus front-motor in Nissan Leaf).
What does this knowledge of the block diagram to me as an owner?
It assists you in understanding how your car operates, in making the best use of it (e.g., charging in the most efficient ways and braking to maximize energy recovery), and in communicating more effectively with your service advisors.
Conclusion: Takeaway
Electric vehicles are reshaping the automotive market and they are posing robust advantages in the dimension of achievement, sustainability, and efficiency. The electric vehicle block diagram can be far more than an engineering icon- it is a roadmap to the actualization of what is uniquely more potent and simpler to operate in an EV. Through this knowledge of this layout, all its users including daily travellers, engineers, policymakers among other users can make better decisions, maximise the use of the vehicles, and be assured of the electric future.
Even in the event that you are drifting further into the world of EVs, you need to focus beyond the shiny front. The system block diagram will bring you the true core of the car-a system whereby all components, the battery pack, the motor and the controller, work together to generate smarter cleaner driving experience.